Portfolio Management Office
For Staff
The Portfolio Management Office (PfMO) is comprised of a team of IT professionals who specialize in managing large and complex projects and who manage a comprehensive project and portfolio management system (PPM). The PPM is the repository for all IT projects and includes project schedules and milestones along with resource allocations.
The team delivers professional project management services across four key disciplines:
- Project Management
- Business Analysis
- Process Improvement
- Change Management
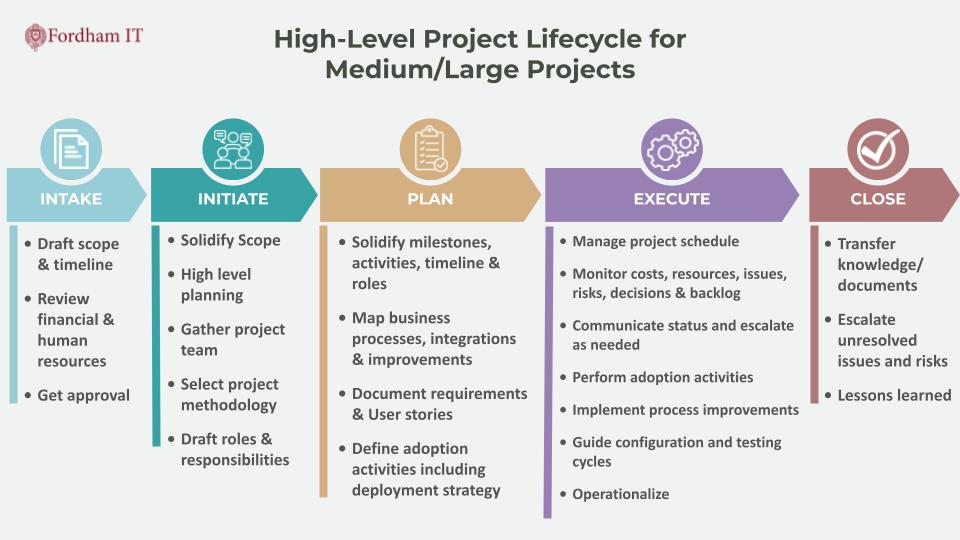
This multifaceted approach equips projects with the necessary talent for success; from project intake to close out. The team performs project request scoping and vetting, develops roles and responsibilities, manages timelines including process improvement and change management activities.
The PfMO plays a pivotal role in achieving successful project outcomes, enhancing organizational efficiency, and meeting strategic objectives. The team ensures that projects are efficiently managed and transitioned smoothly into operations with new processes and techniques that aid the successful adoption of solutions.
Project and Portfolio Management
TeamDynamix is the system used by the PfMO for project and portfolio management (PPM). It is the repository for all IT projects and provides insights into the size and variety of projects underway. Fully leveraged, it facilitates resource and capacity management while also enabling the strategic accomplishment of key priorities.
-
Project managers coordinate and oversee the process of a project from start to finish. When a project is approved to launch, the project manager assembles the team and gathers information to create the project plan and schedule. Using the plan as the basis for monitoring progress, the project manager works to help the team maintain focus on the work at hand and facilitates status meetings and reports, keeping the team and stakeholders informed about the project’s progress. The project manager serves as a central point of contact for the team, vendors, and other stakeholders. As problems arise, the project manager documents the issues and monitors them through resolution. If the project team needs additional resources, such as staff or funding, the project manager escalates these needs to the project sponsor. All the while, the project manager provides oversight while the project is in motion to guide the team toward achieving the intended outcomes.
-
Business Analysis is the starting point for all project request inquiries. Analysts complete a quick-start Scope document that outlines the objectives of the project request, primary deliverables, cost estimates, high-level timeline, and hour estimates for required resources. When a project request is approved, analysts work closely with stakeholders and project team members to document current processes and requirements and then develop future processes with input from the team which includes a process improvement professional. Analysts develop all technical documentation in collaboration with vendors and internal team members. They document system configurations and manage testing cycles to facilitate system readiness for production. They partner with other PfMO team members to operationalize support for projects post go-live.
-
Process improvement managers play an integral role in selected projects by helping to configure and implement new technologies to effectively realize efficiencies. They work closely with business analysts and subject matter experts to analyze current processes and to streamline and update them to take advantage of newer technologies and methods. Analysis of areas for improvement starts with an impact analysis and review of key metrics. It is followed by holding brainstorming sessions with project team members to identify major pain points and solutions and to help plan out how those improvements will be implemented and adopted. Process improvement managers also participate in the continuous improvement of PfMO processes.
-
Change managers are key to the realization of the efficiencies envisioned when a new technology is implemented or an existing technology or process will be substantially changed. They focus on understanding who is impacted by the new or changed technology and how their work routines will change. Change managers then formulate communication plans to assist project stakeholders in the creation of clear messaging that contains technology specific highlights. Change managers are also responsible for professional training development and orchestrating technology deployments in lockstep with the project manager. This role is integral to the overall project team’s success.